Educational Resources
Cancer Genomics Consortium Educational Resources
Here, you will find comprehensive and up-to-date information aimed at enhancing the understanding and expertise in clinical cancer genomics. Our resources are designed for clinical and research professionals, offering insights into the latest in cancer genomics.
Q16. What defines the threshold for quantitative real-time PCR?
A. Amount after 10 cycles
B. #of cycles for log-linear
C. Slope of amp curve
D. #of cycles for plateau
Correct answer: B
Explanation of answer: The cycle-threshold is defined as the fractional cycle number in the log-linear region of PCR amplification in which the reaction reaches fixed amounts of amplicon DNA.
Q15. Which karyotype if found in a 32-year-old woman with a normal phenotype, would explain her history of recurrent pregnancy loss?
A. 45,x
B. 46,xx
C. 46,XX,+13,der(13;14)
D. 46,XX,t(11;13)
Correct answer: D
Explanation of answer: Balanced translocations are a common finding in normal phenotype parents with recurrent pregnancy loss.
Q14. What is the PRIMARY reason that the cytogenetics lab needs to know the possible diagnosis when processing a newly received bone marrow sample?
A. CAP requirement
B. Cell culture conditions
C. Know amount needed
D. Reimbursement
Correct answer: B
Explanation of answer: Knowing the reason for referral is important for cell culture selection.
Q13. A 5 yr old being evaluated for ALL. The ped onc orders FISH: nuc ish(ABL,BCR)x2,(KMT2Ax3),(ETV6x3,RUNX1x4) [166/200]. What does it mean?
A. Likely mosaic for triploid line
B. Positive for ETV6::RUNX1
C. Suggestive of hyperdiploidy
D. Evidence of iAMP21 B-ALL
Correct answer: C
Explanation of answer: When multiple probes demonstrate copy gains, the most likely answer is a hyperdiploid karyotype; however, it is important to demonstrate this subtype by either multiple centromere probes (FISH) or by karyotype.
Q12. A 70 yo female with suspected MDS has the result: 46,XX,del(5)(q13q33)[4]/47,XX,+8[4]/46,XX[12]. What does this mean?
A. 40% had del chr 5, extra chr 8
B. There were two unrelated abnormal clones
C. There were two related abnormal clones
D. 40% had dels of chrs 5 & 8
Correct answer: B
Explanation of answer: This is a question about how to read the ISCN properly. Because there is no indication of acknowledgment of a stemline in the second set of cells, this indicates that there are two separate abnormal populations of cells comprising a total of 40% of the cells. The remaining 12 (60%) are normal. While one may expect to see the clones as related in disease, it is possible the two lines either appeared separately or they may represent subclones in the main disease line with another genetic driver (e.g. SF3B1 as the driver with one subclone with del(5q) and the other subclone +8). Using just the karyotype, one cannot differentiate between these two possibilities.
Q11. What tumor type is likely to generate this karyotype?
A. Osteosarcoma
B. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma
C. Synovial Sarcoma
D. Atypical lipomatous tumor
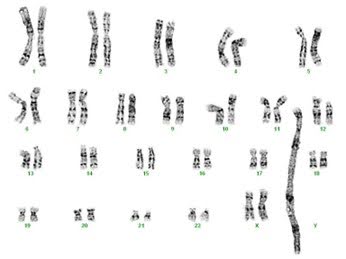
Correct answer: B
Explanation of answer: Amplification of MDM2, CDK4 can be useful to distinguish Atypical lipomatous tumor/well-differentiated liposarcoma and Dedifferentiated liposarcoma from benign tumors. These amplifications are generally detected as supernumerary rings and giant marker chromosomes on karyotype.
Q10. Paired tumor/normal NGS was performed on a bone marrow specimen from a pediatric patient with cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. A CEBPA mutation was identified, c.175G>T p.(Glu59Ter). This finding suggests that the patient has:
A. A favorable prognosis
B. A germline CEBPA variant
C. An undetected 3' mutation
D. A high p30:p42 ratio
Correct answer: D
CEBPA-mutated acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is its own diagnostic category within the WHO Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumors. Current literature supports the presence of CEBPA biallelic mutations (i.e., biCEBPA) or single mutations located within the 3' basic leucine zipper (bZIP) region of the gene (i.e., smbZIPCEBPA) as favorable, whereas single mutations found outside of this bZIP region do not have a more favorable prognosis (as compared with CEBPA-wildtype AML). Thus, answer A would not be correct. N-terminal CEBPA mutations have been shown to occur in the germline of individuals with AML at a higher frequency than variants located within other regions of the gene. Although in a tumor-only test setting the location of this variant in the N-terminus of CEBPA would support further investigation into the origin of this variant, the paired tumor/normal design of the NGS assay confirms that this N-terminal variant is somatic. Thus, answer B would not be correct. Although biallelic CEBPA mutations are commonly identified in CEBPA-mutated AML, single mutations are not uncommon. Thus, although technically possible, answer C is not the best answer. The CEBPA protein exists as two primary isoforms, a full-length isoform (p42) and a shorter isoform (p30). Due to the fact that CEBPA has two translation initiation sites, the presence of a truncating N-terminal variant often results in a decrease of the p42 isoform and increase in the p30 isoform. This leads to an increased p30:p42 ratio which drives an immature cell state. Thus, D is the correct answer.
Q9. A young patient presented with a thigh mass. Histologic examination showed a small round blue cell tumor. FISH studies with the EWSR1 break-apart probe were performed. Based on the result of the FISH studies, select the correct answer:
A. This is a normal result
B. Rearrangement of EWSR1
C. Rhabdomyosarcoma
D. Synovial sarcoma
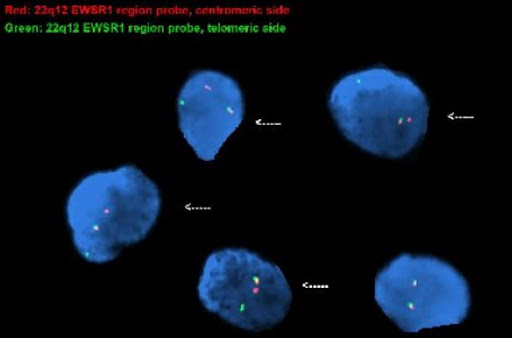
Correct answer: B
Explanation of answer: This is an abnormal signal pattern consisting of one intact (fused) signal, one 5’ (centromeric) signal, and one 3’ (telomeric) signal indicating a rearrangement of 22q12 (EWSR1) region; consistent with the diagnosis of Ewing’s sarcoma. PAX3::FOXO1 or PAX7::FOXO1 translocations are present in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Spindle cell / sclerosing rhabdomyosarcoma may harbor MYOD1 mutations or VGLL2::NCOA2 rearrangements. Synovial sarcoma is characterized by a specific SS18::SSX fusion gene.
Q8. A 4-year-old boy had bilateral lung cysts and cystic nephroma. A splicing variant was detected in a hereditary cancer NGS panel and tumor biopsy showed another frameshift variant in the same gene at 15%. What function is the gene involved?
A. DNA mismatch repair
B. Homologous recombination
C. RNA splicing
D. Gene silencing
Correct answer: D
The clinical presentation suggests the causative gene is DICER1 which encodes a protein that facilitates microRNA production. microRNA is an important mechanism that regulates gene expression by silencing mRNA at post-transcription level.
Q7. New B-lymphoblastic leukemia case: Based on genetics what result(s) has a very favorable prognosis?
A. t(4;11)(q21;q23)
B. t(12;21)(p13.2;q22.1)
C. Hypodiploid karyotype
D. t(9;22)(q34.1;q11.2)
Correct answer: B
Out of these options, for B-ALL t(12;21) is the only favorable prognosis. Hyperdiploid karyotype is also a favorable prognosis.
Q6. What FISH panel would you order for myeloid neoplasms?
A. Chr. 5, 7, 8, 17, 20
B. Chr. 11, 12, 13, 17
C. Chr. 5, 11, 13, 17, 20
D. Chr. 1, 13, 14, 17
Correct answer: A
Alterations commonly seen in myeloid malignancies include deletion 5q, 7q, monosomy 5, 7, trisomy 8, deletion 20q and deletion 17p/monosomy 17.
Q5. During a surgical pathology rotation, you are asked to send a sample on a patient who might have a soft tissue tumor for cytogenetic G-band analysis. Which of these samples would you send to the lab?
A. Blood
B.Fresh tissue
C.Frozen tissue
D.Formalin fixed tissue
Correct answer: B
For a solid tumor, such as soft tissue tumor, the best tissue for cytogenetic testing by karyotype is the fresh tumor tissue. The FFPE is fixed and therefore cannot be cultured. The frozen will most likely not grow as the cells are dormant/dead. The blood will not have tumor cells that can be cultured.
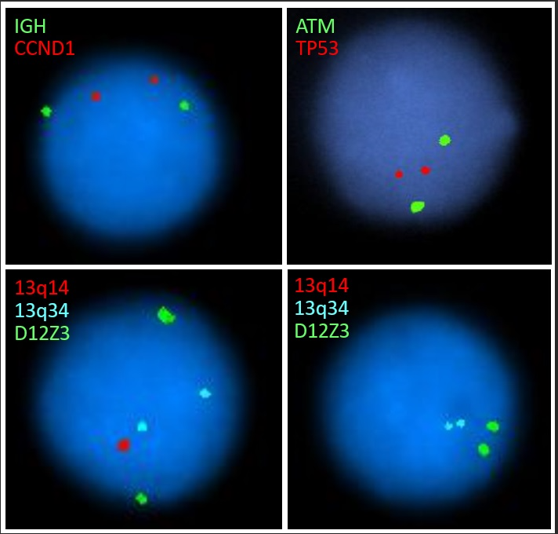
Q4. The following CLL FISH panel result is from a 77 year old man referred due to an elevated white blood cell count. Based on the representative images, which statement is correct?
A.This result is consistent with mantle cell lymphoma
B.This result is associated with a good prognosis in CLL
C.This result is not specific for CLL
D.This result is associated with the most adverse prognosis in CLL
Correct answer: B
This patient has both heterozygous and homozygous deletion of 13q14. This is a common finding in CLL. Patients with a 13q deletion as the sole abnormality detected by FISH generally have the longest survival time. Prognosis for patients with a homozygous 13q deletion is not significantly different than for a heterozygous 13q deletion (PMID: 22139735). Some newer data suggests that larger deletions may have less favorable outcomes (PMID: 34522485).
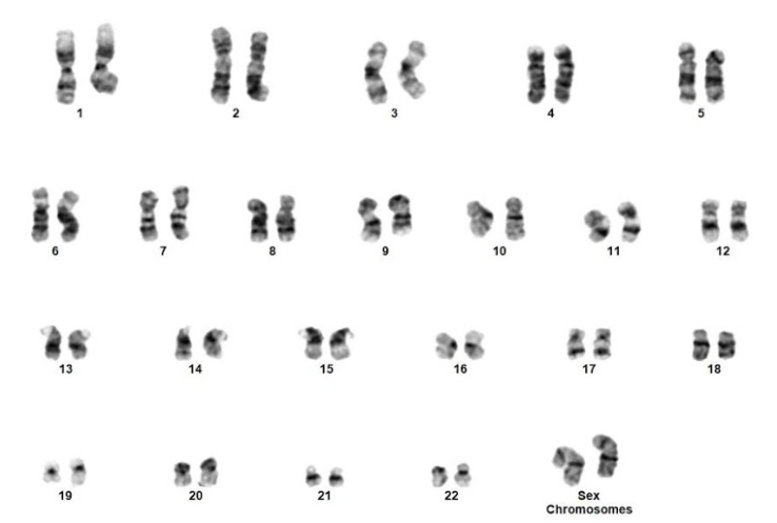
Q3. A female with a history of AML post transplant with a male donor has presented with the following karyotype. Which of the following is true based on the karyotypic abnormality?
A. Associated with a good prognosis for the patient
B. Auer rods are commonly present
C. Basophilia is commonly present
D. Monosomy 7 is a common secondary finding
Correct answer: D
The inv(3)(q21q26) is often associated with a fusion between RPN1 and MECOM (MDS1 AND EVI1 COMPLEX LOCUS). It has been described in AML and MDS. Monosomy 7 is a common secondary abnormality. It is associated with a negative impact on prognosis.
Q2. According to the American College of Medical Genetics Laboratory Technical Standards and Guidelines, how long should images from neoplastic FISH cases be retained?
A. Two weeks after the report has been signed
B. Three years
C. Ten years
D. Twenty years
Correct Answer: C
In general, "critical records" for cytogenetic testing are kept for 20 years. However, there is variability depending on the technology utilized and reason for referral.
Current guidelines specify the following retention times:
- Processed patient specimens and/or cell pellets – 2 weeks after report has been signed
- Stained slides (e.g., G-banding) – 3 years
- Neoplastic FISH Images – 10 years
- Images (chromosome analysis/non-neoplastic FISH) – 20 years
- Array – recommended that primary data be stored for at least 2 years and the analysis file + final clinical report be kept for “as long as possible”
(Shao, et al., 2021)
Q1. NGS has been widely used to identify germline variants for diagnosing hereditary cancer syndromes. However, it may also detect mosaic variants that may be acquired due to clonal hematopoiesis of intermediate potential (CHIP). Which of the following cancer genes is most likely to be involved in CHIP?
A. TP53
B. DICER1
C. PTEN
D. BRCA2
Correct answer: A
CHIP is associated with aging in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and the most commonly variants have been seen in DNMT3A, TET2, ASXL1, JAK2 and TP53. TP53 is one of the most commonly tested gene in hereditary cancer panel, therefore, skewed allele frequency in TP53 may indicate an event of CHIP, which needs to be differentiated from Li-Fraumeni syndrome. PMID: 31827082